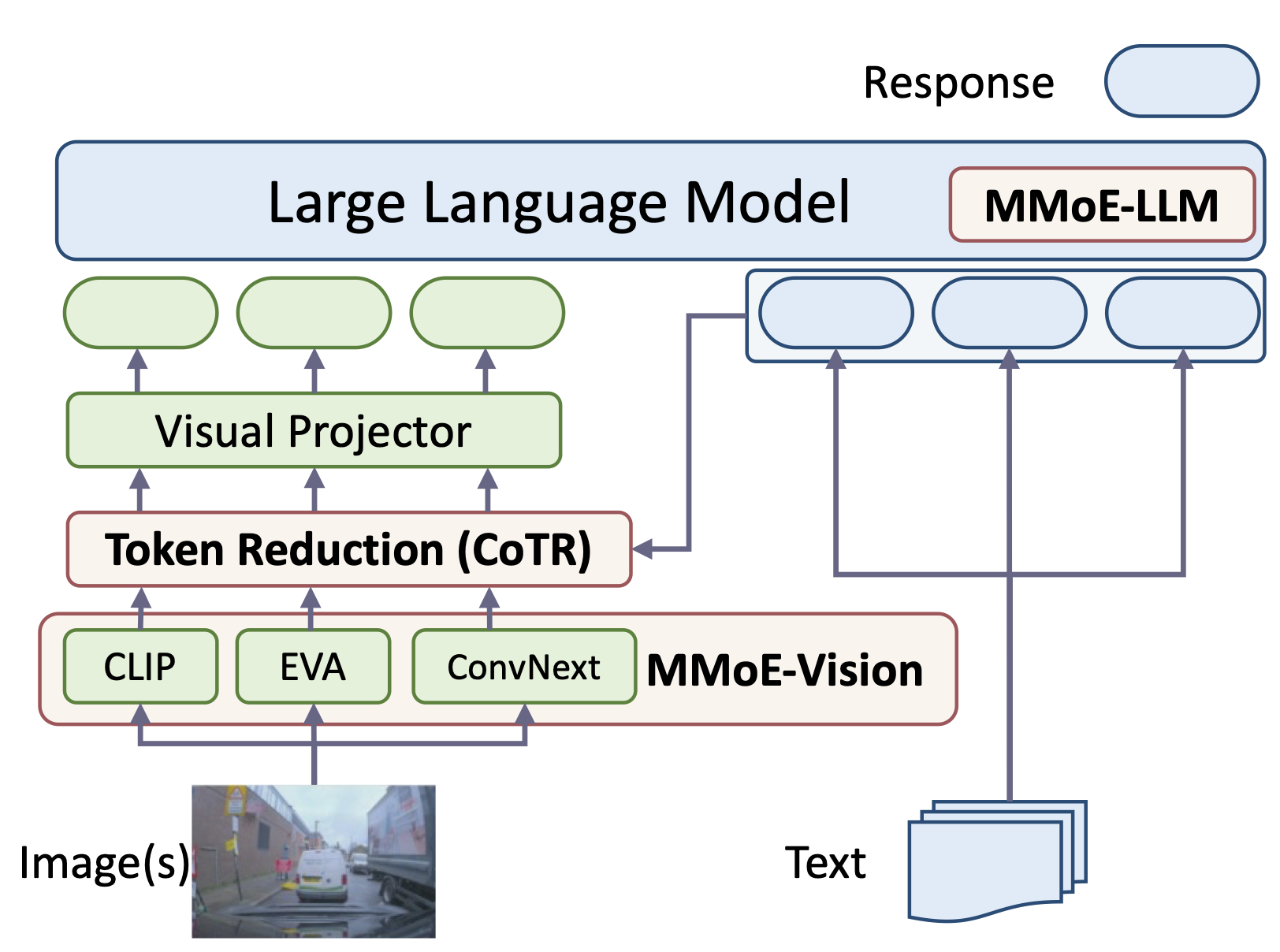
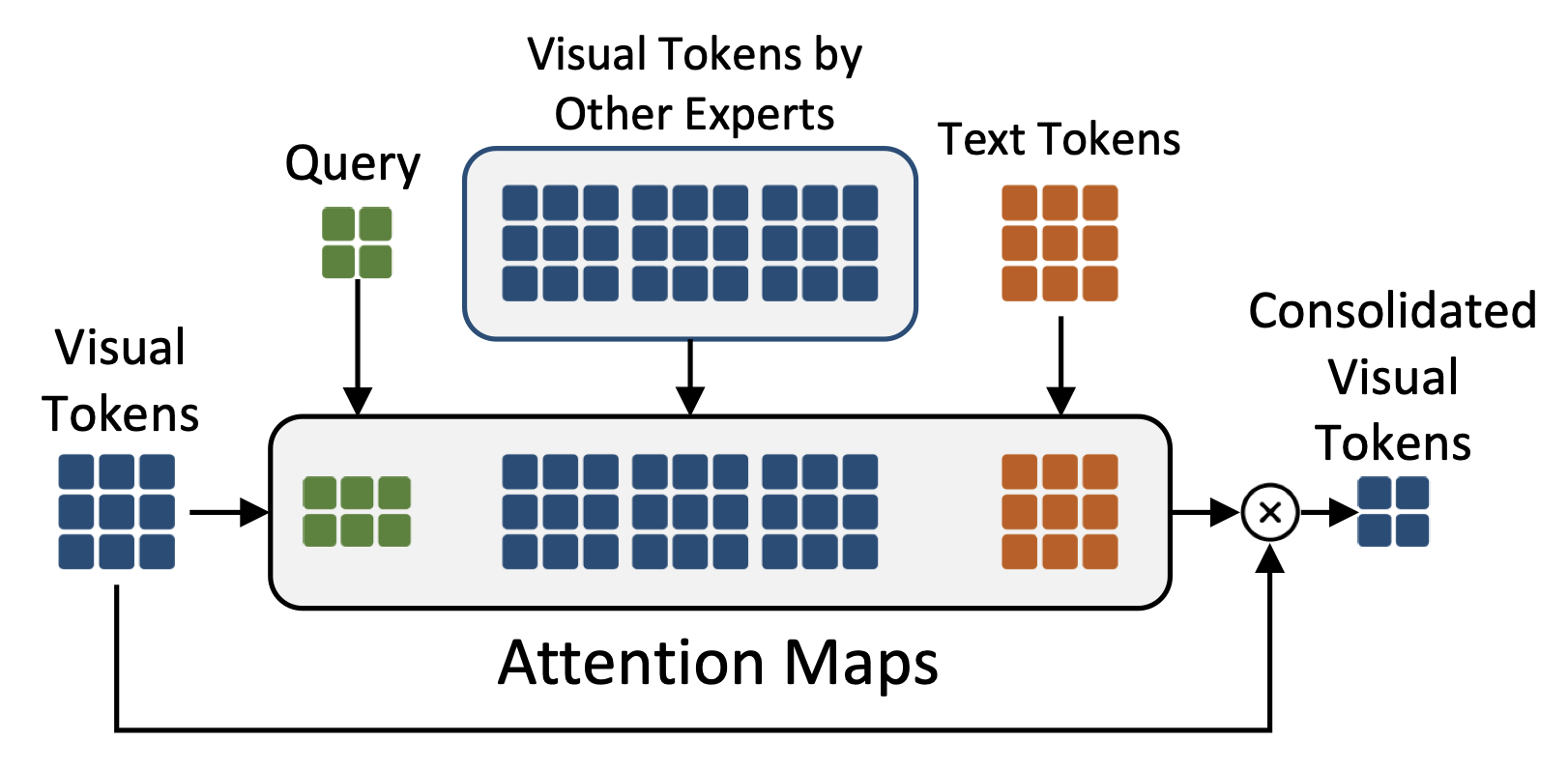
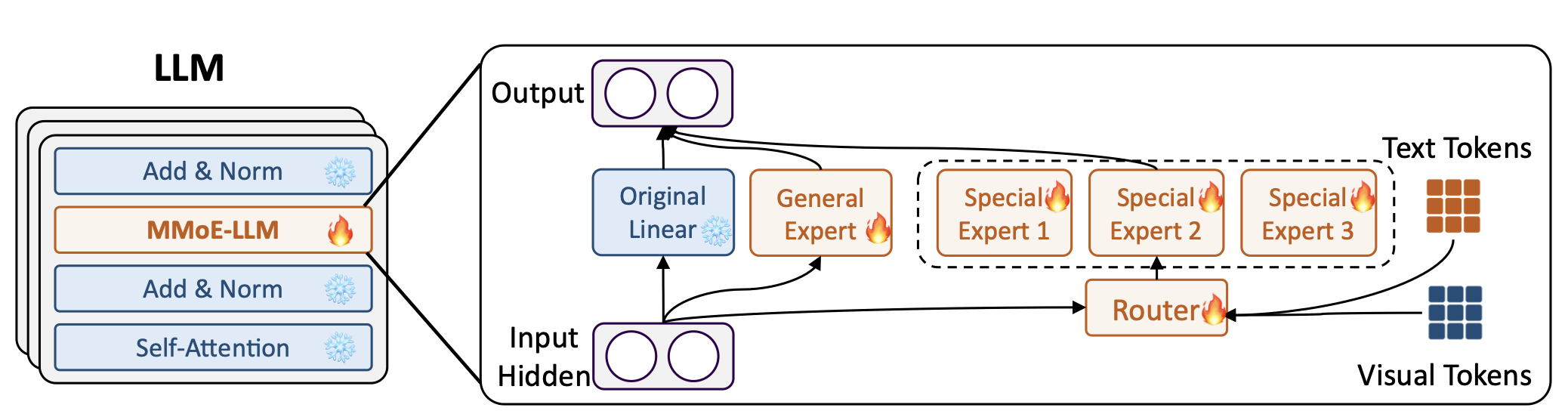
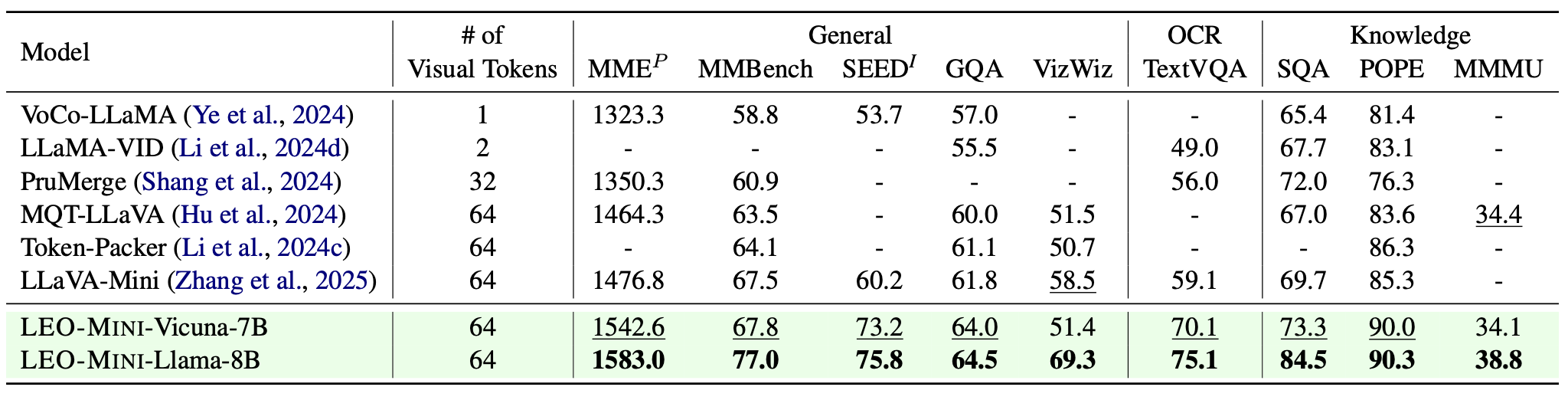
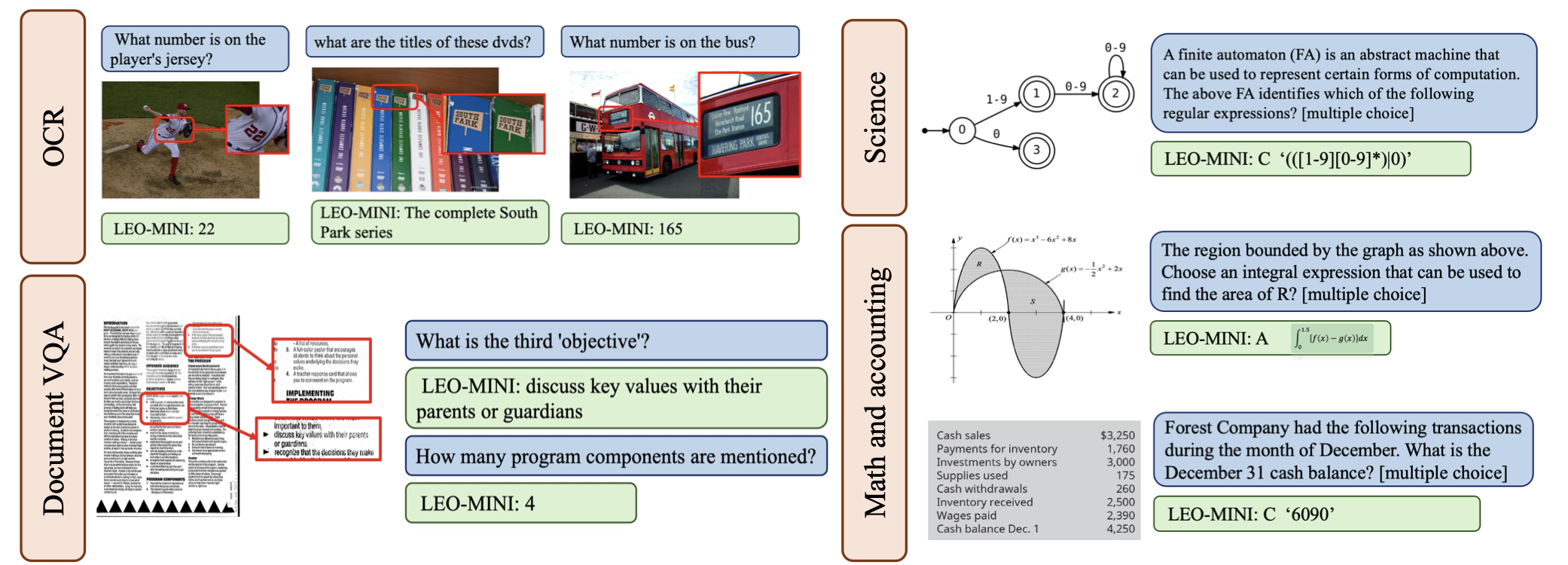
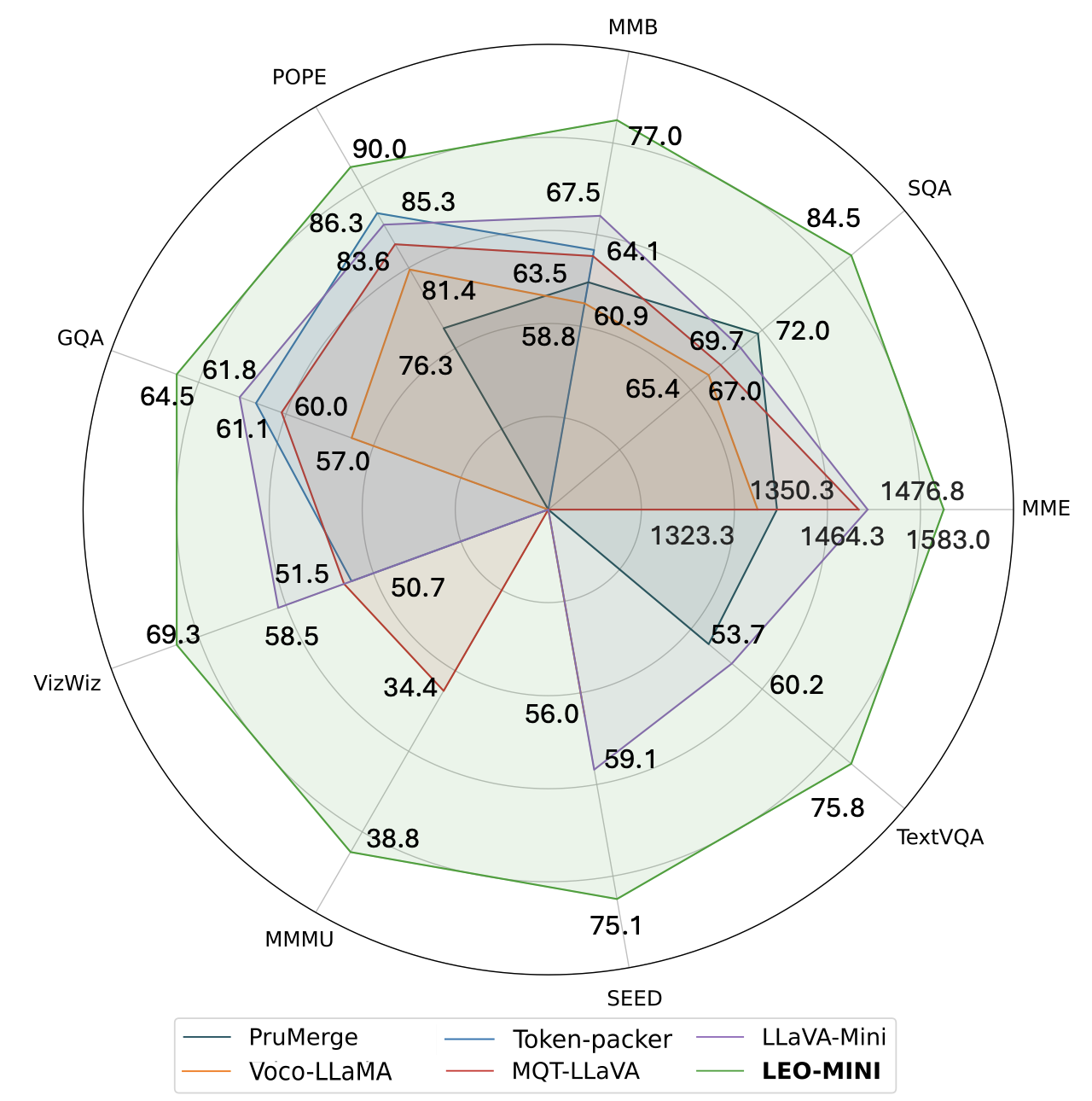
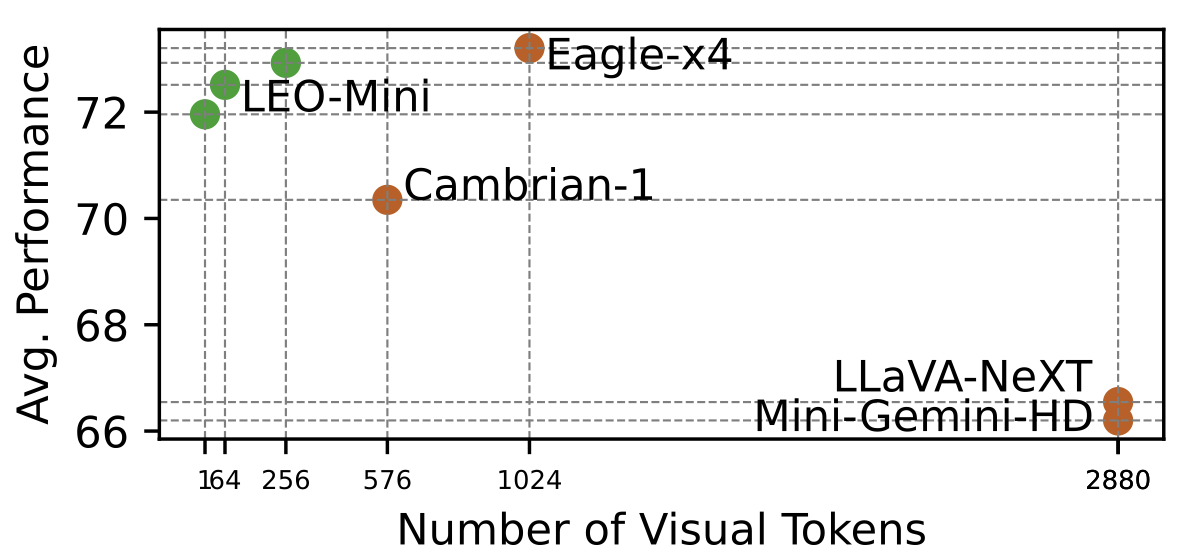
Redundancy of visual tokens in multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) significantly reduces their computational efficiency. Recent approaches, such as resamplers and summarizers, have sought to reduce the number of visual tokens, but at the cost of visual reasoning ability. To address this, we propose LEO-Mini, a novel MLLM that significantly reduces the number of visual tokens and simultaneously boosts visual reasoning capabilities. For efficiency, LEO-Mini incorporates CoTR, a novel token reduction module to consolidate a large number of visual tokens into a smaller set of tokens, using the similarity between visual tokens, text tokens, and a compact learnable query. For effectiveness, to scale up the model's ability with minimal computational overhead, LEO-Mini employs MMoE, a novel mixture of multi-modal experts module. MMoE employs a set of LoRA experts with a novel router to switch between them based on the input text and visual tokens instead of only using the input hidden state. MMoE also includes a general LoRA expert that is always activated to learn general knowledge for LLM reasoning. For extracting richer visual features, MMoE employs a set of vision experts trained on diverse domain-specific data. To demonstrate LEO-Mini's improved efficiency and performance, we evaluate it against existing efficient MLLMs on various benchmark vision-language tasks.